A report of three cases of surgical removal of esophageal schwannomas
Introduction
Benign primary tumors of the esophagus are uncommon; most cases of benign esophageal tumors include leiomyomas and cases of esophageal schwannomas are extremely rare. We report three cases that were diagnosed with a leiomyoma pre-operatively, but all the tumors were identified as a schwannoma on post-operative pathology (Table 1). The nearest patient underwent thoracoscopical surgery and the other two patients underwent right thoracotomy.

Full table
Case representation
Case 1
A 46-year-old man presented with a 1-month history of discomfort during swallowing. He was hospitalized at Henan Cancer Hospital on 03/12/2015 due to severe dysphagia after an esophageal lesion was detected by esophageal endoscopy at another hospital. His medical and family histories were unremarkable. Esophageal endoscopy showed two mucosal protrusions with normal esophageal mucosa extending 25–29 cm from the incisors, with sizes of 22.2 mm × 12.7 mm, 16.1 mm × 11.7 mm (Figure 1A). Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) showed two hypoechoic tumors in the muscularis propria layer (Figure 1B). EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) revealed an esophageal leiomyoma. Enhanced thoracic computed tomography (CT) showed a mass in the middle esophagus with slight enhancement (Figure 1C). Esophagography showed a protruding smooth mass in the middle thoracic esophagus (Figure 1D).
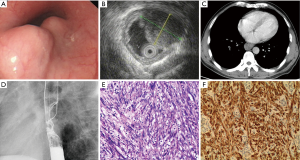
The patient underwent thoracoscopic enucleation of the tumor through the right chest on 03/17/2015. We chose a 30-degree left lateral recumbent position, used a single lumen endotracheal intubation and two-lung ventilation, and then provided the thoracic cavity with carbon dioxide positive pressure using an enclosed trocar to make the lungs collapse. For the incision, we chose the mid-axillary line the 4th and 7th intercostal space, and the lower edge of the subscapula and the 9th intercostal space scapula line, which can be adjusted according to the specific circumstances of the patient. Two small tumors were found adjacent to the mid-thoracic esophagus without lymph glands. The muscle of the esophagus was detached and the tumor was excised. Intraoperative endoscopy was used for careful examination of the mucosa. We closed the muscular layer after enucleation by hand-sewing.
The two tumors were well-demarcated and had a globular appearance, measuring 30 mm × 20 mm × 17 mm and 30 mm × 18 mm × 15 mm. Histopathological findings revealed spindle-shaped cells in long fascicles (Figure 1E). Immunohistochemical staining revealed the tumor was positive for S-100 protein (Figure 1F), but negative for smooth muscle actin (SMA), Dog-1, CD117, muscle-specific actin (MSA), cytokeratin (CK), anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), c-Kit, and CD34, and had a low proliferation rate (Ki-67 index of less than 10%). The patient started oral feeding at post-operative day (pod) 1 and was discharged on pod 5. The patient remains free of recurrence 1 year after the operation, and esophagography findings are normal.
Case 2
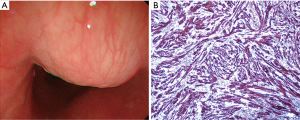
A 42-year-old woman had been suffering from dysphagia for 2 months. Her medical and family histories were unremarkable. Esophageal endoscopy demonstrated a submucosal tumor without ulceration, extending 17–19 cm from the incisors (Figure 2A). Immunohistochemical staining revealed the tumor was positive for S-100 protein (Figure 2B), vimentin, nestin, and CD68, but was negative for Dog-1, CD117, CK, desmin, ALK, c-Kit, and SMA. The blood vessels were positive for CD34, and there was a low proliferation rate (Ki-67 index of less than 5%). The patient started oral feeding on pod 4 and was discharged on pod 12. The patient remains free of recurrence 4 years after the operation.
Case 3
A 58-year-old woman was admitted to our hospital with a 2 months’ history of dysphagia. Her medical and family histories were also unremarkable. Esophageal endoscopy demonstrated a submucosal eminentia neoplasm without ulceration, extending 22–30 cm from the incisors (Figure 3A). Immunohistochemical staining revealed the tumor was positive for S-100 protein (Figure 3B), vimentin, nestin, and neuron-specific enolase (NSE), but was negative for Dog-1, CD117, CK, and desmin. The patient started oral feeding on pod 9 and was discharged on pod 14. The patient remains free of recurrence 5 years after the operation.

Discussion
Most tumorous lesions of the esophagus are either squamous cell carcinomas or adenocarcinomas, and benign tumors are uncommon. Benign schwannoma of the esophagus is rare, with leiomyomas accounting for 80% of cases (1). There have been only 28 reported cases in China in the literature. Schwannoma of the esophagus more frequently occurs in women than in men. The symptom that our three cases presented with was dysphagia. However, a wide variety of presentations have been reported, including dyspnea, chest pain, and coughing because of trachea compression (2-4).
CT and esophagography just provide the location of the lesion. Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) is useless for assessing whether these lesions are benign or malignant because the FDG accumulation level in malignant schwannomas has not been clarified (5,6). EUS-FNA might be able to provide a diagnosis. However, there have been no reports of diagnosis of an esophageal schwannoma before surgery, because diagnosis by biopsy is difficult owing to the submucosal benign tumor morphology. The main reason is a shortage of tissue, but EUS-FNA is necessary for excluding esophageal cancer. All the three cases were diagnosed esophageal leiomyoma before operation. The final diagnosis of benign esophageal schwannoma is based on histopathology and immunohistochemistry. The identification of a neurogenic tumor cell origin is by positive immunostaining for S-100 and vimentin (1-3,5-8). Smooth muscle markers, such as actin and desmin, are negative in this tumor. CD34 and c-Kit, characteristically positive in gastrointestinal stroma tumors (GIST), are also negative. The histological criteria for the diagnosis of malignant schwannoma are based on a combination of the presence of mitotic figures, nuclear atypia, and other biological characteristics. The tumors in our three patients showed no evidence of invasiveness. Otherwise, there are two tumors in the first case and there were no related reports in the previous studies.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are ineffective, and the most common treatment is enucleation by surgery or endoscopy (1,9). In the cases we report here, we enucleated the tumor under thoracoscopy in the first patient and through right thoracotomy in the other two patients. In fact, there was no clear basis for the choice of surgery method; it is just because we have gained experience of thoracoscopy between the second and third patient. Extended lymph node dissection was not performed in the three cases, because all of the preoperative diagnoses were esophagus leiomyoma, and there were not any increscent lymph nodes around the thorax cavity. Thoracoscopic resection is advantageous because it is less invasive, therefore shortening the hospital stay, and reducing pain at the surgical wound site (8,10). A retrospective study showed that minimally invasive resection of benign esophageal tumors is technically safe and associated with a shorter length of stay compared with open approaches. Although no specific cutoff for size could be identified, most tumors greater than 7 cm were removed by thoracotomy (11). Intraoperative endoscopy is particularly helpful for careful examination of the mucosa, and hand-sewn suturing is also recommended for closure of the muscular layer after enucleation.
Conclusions
Here, we report three cases of schwannoma of the esophagus, all of whom underwent enucleation surgery. One was enucleated by thoracoscopy, and the other two through right thoracotomy. In comparison, thoracoscopy surgery is less invasive, with a shorter length of hospital stay, and reduced pain at the surgical wound site.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their deep gratitude to Prof. Li., Prof. Liu, Haibo Sun, and Zongfei Wang for their support.
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Informed Consent: Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
References
- Kitada M, Matsuda Y, Hayashi S, et al. Esophageal schwannoma: a case report. World J Surg Oncol 2013;11:253. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva V, Chawla K. Giant schwannoma of upper esophagus requiring esophagectomy. Ind J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2008;24:203-5. [Crossref]
- Kassis ES, Bansal S, Perrino C, et al. Giant asymptomatic primary esophageal schwannoma. Ann Thorac Surg 2012;93:e81-3. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Dutta R, Kumar A, Jindal T, et al. Concurrent benign schwannoma of oesophagus and posterior mediastinum. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2009;9:1032-4. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Sato S, Takagi M, Watanabe M, et al. A case report of benign esophageal schwannoma with FDG uptake on PET-CT and literature review of 42 cases in Japan. Esophagus 2012;9:165-71. [Crossref]
- Makino T, Yamasaki M, Takeno A, et al. Thoracoscopic enucleation of esophageal schwannoma exhibiting (18) F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on positron emission tomography. Dis Esophagus 2013;26:331-2. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Matsuki A, Kosugi S, Kanda T, et al. Schwannoma of the esophagus: a case exhibiting high 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in positron emission tomography imaging. Dis Esophagus 22:E6-E10. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Toyama E, Nagai Y, Baba Y, et al. A case of thoracoscopically resected benign esophageal schwannoma with high uptake on FDG-PET. Esophagu 2008;5:167. [Crossref]
- Naus PJ, Tio FO, Gross GW. Esophageal schwannoma: first report of successful management by endoscopic removal. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;54:520-2. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi S, Inoue K, Imagawa A, et al. Benign esophageal schwannoma compressing the trachea in pregnancy. Ann Thorac Surg 2008;85:660-2. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Kent M, d'Amato T, Nordman C, et al. Minimally invasive resection of benign esophageal tumors. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;134:176-81. [Crossref] [PubMed]


