AB 88. Balf changes of CD4+, CD8+ cells in lung cancer patients with different hemotherapeutic regimens
Background: Reports point out acute lung toxicity of chemotherapeutic agents in cancer patients. The aim of our study was to assess BALF and lung function findings of the 3 most applied platinum-based regimens for the treatment of metastatic lung cancer.
Methods: Within one year period 20 patients (ECOG 0,1) agreed to participate the study, but 15 were evaluable (5 patients died from disease progression, before reassessment). Patients underwent lung function tests and BAL, of the opposite to the tumor lung, during diagnostic bronchoscopy before and after 6 chemotherapy courses. Platinum-based regimens were combination of vinorelbine (VN) 6 patients, gemcitabine (GEM) 4 patients and etoposide (EP) 5 patients.
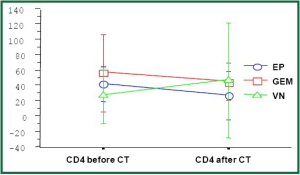
Results: All patients, but one were males and smokers (93%). Median patients’ age was 56 years (42-75) and median pack-years 80 (40-120). No significant difference was noted in the patients’ age between the 3 treated groups. No significant changes in CD4+ and CD8+ cells were noted between the 3 groups of treatment. However, changes were noted within each group only for CD4+ cells: VN before vs. after P=0.05; GEM before vs. after P=0.03; EP before vs. after P=0.3. For CD8+ no significant changes were noted. Also no changes were noted in lung function tests (FEV1, FVC) between or within the groups (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Although our number of patients is small due to recruitment difficulties in such patient population, changes were noted in BALF CD4+ cells for the 3 most applied regimens.